Piping engineering is a critical discipline in the oil and gas, petrochemical, power, and process industries. It involves the design, layout, analysis, fabrication, and installation of piping systems that safely transport fluids and gases across industrial facilities. Understanding the key phases in piping engineering and execution is essential for successful project delivery, ensuring safety, functionality, and compliance with industry standards.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the most important phases in piping engineering and execution, breaking them down into clear and practical steps followed across the project lifecycle.

Important Phases in Piping Engineering and Execution
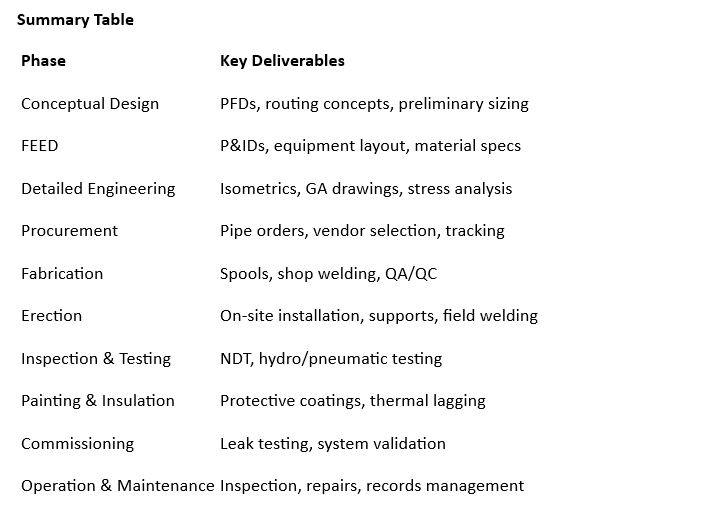
1. Conceptual and Feasibility Study
- Determine the need for piping systems.
- Identify the type of fluids, flow rates, pressure, temperature, and layout constraints.
- Evaluate project feasibility, budget, and preliminary routing.
2. Basic Engineering (Front-End Engineering Design – FEED)
- Preliminary Process Flow Diagrams (PFDs) and Piping & Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs).
- Estimate pipe sizes based on flow requirements.
- Initial layout of equipment and plot plan.
- Preliminary material selection and specifications.
3. Detailed Engineering
- Develop full P&IDs with instrumentation and control details.
- Create piping layouts, GA drawings, and isometric drawings.
- Perform piping stress analysis and flexibility analysis.
- Select pipe materials (as per PMS – Piping Material Specification).
- Define pipe classes, support types, insulation, and painting systems.
- Finalize MTO (Material Take-Off).
4. Procurement
- Issue RFQs (Request for Quotations) for pipes, fittings, flanges, valves, gaskets, and supports.
- Evaluate vendors and approve quality documentation.
- Purchase and track delivery of materials.
- Conduct Factory Acceptance Testing (FAT) for critical components.
5. Piping Fabrication
- Cut, bevel, and weld pipes in workshops as per isometric drawings.
- Prepare pipe spools and tag them for installation.
- Perform Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) on welds.
- Maintain fabrication records and QA/QC logs.
6. Piping Erection (Site Installation)
- Transport prefabricated spools to site.
- Install pipes, supports, valves, and inline equipment.
- Field fit-up and site welding as required.
- Ensure alignment and tolerance control.
- Perform in-place NDT on site welds.
7. Inspection and Testing
- Conduct hydrostatic or pneumatic pressure testing.
- Perform visual, radiographic, and ultrasonic inspections.
- Verify line cleanliness through flushing, pickling, or blowing.
- Ensure compliance with codes (e.g., ASME B31.3) and project specs.
8. Painting and Insulation
- Apply protective coatings (anti-corrosion, fireproofing).
- Insulate hot or cryogenic lines to prevent heat loss/gain.
- Add cladding or jacketing for protection.
9. Pre-Commissioning and Commissioning
- System flushing, air blowing, and drying.
- Leak testing and final tightening.
- Pressure and functional tests on valves and instrumentation.
- P&ID walk-downs and punch list resolution.
- Handover to operations with as-built documentation.
10. Operation and Maintenance
- Periodic inspection and monitoring.
- Corrosion control and cathodic protection.
- Pipe replacement or rerouting during upgrades.